Last Updated on June 10, 2025 by Admin
One common error you might spot in Google Search Console is “Duplicate without user-selected canonical.” This error occurs when search engine found duplicate content across website and doesn’t find proper canonical tag. This excluded the page from serp, leaving a direct impact on your website’s visibility.
What is the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error?
The “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status in Google Search Console appears when canonical tag is missed from the page that indicates Google for primary page content, then it will not be indexed due to duplicity with other pages. This can lead to indexing issues and weaken your SEO efforts when important pages get excluded from search results. It is crucial to fix this issue immediately to avoid losing potential traffic.
What causes the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status?
Several factors can trigger this error and it is necessary to identify the exact cause on your website since the right solution depends on it.
- Content duplication
- Missing canonical tags
- Location-based pages
- Syndicated & paginated content
- Additional issues of conflicting HTTP/HTTPS page, WWW vs non-WWW domain, and URL parameters.
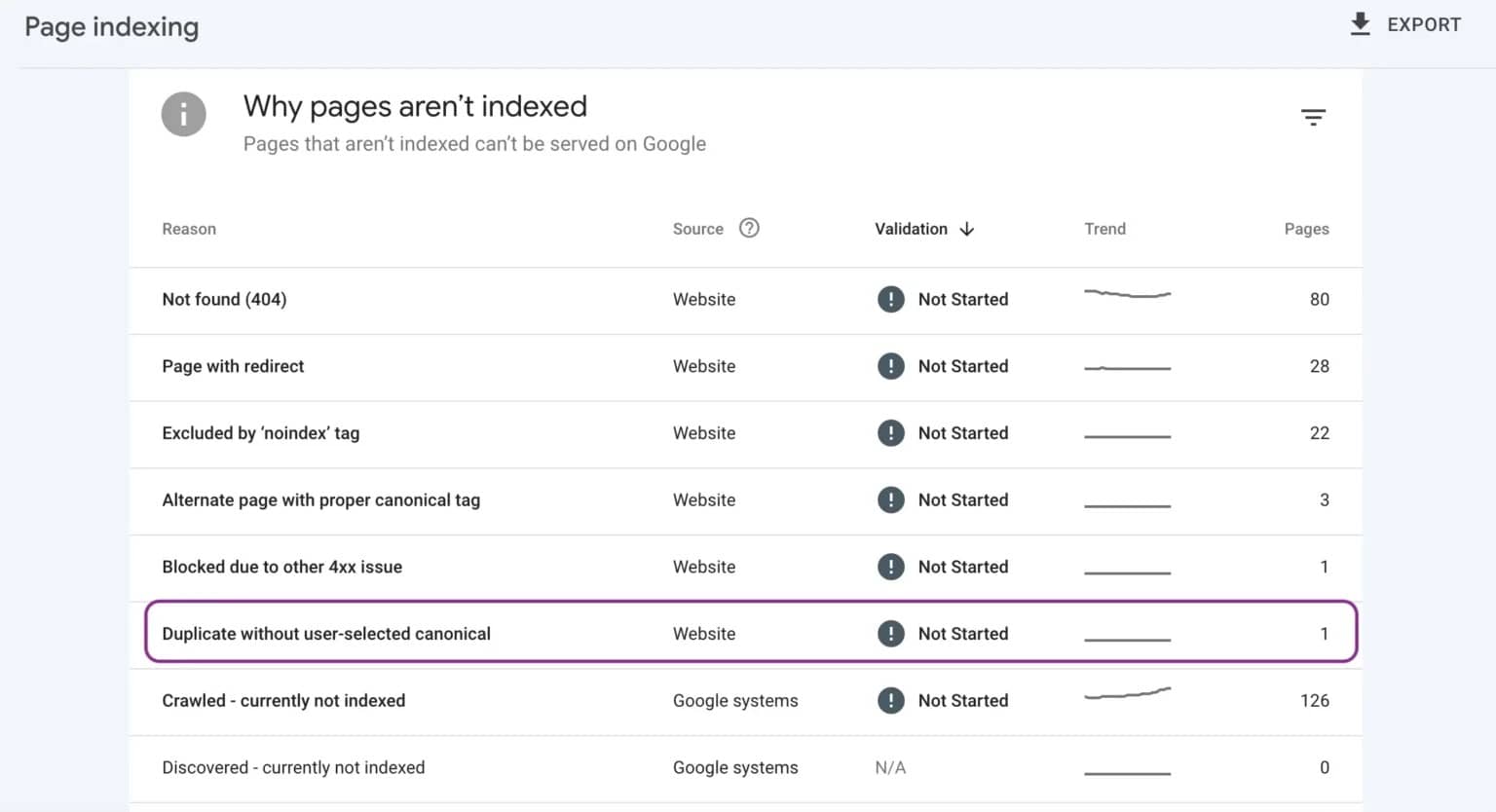
How to find canonical issues in Google Search Console?
Follow the below steps to check if your site has been affected by the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error:
- Log into Google Search Console, and navigate to the “Pages” report.
- You will see a chart showing both indexed and not-indexed pages.
- Click on the “Not indexed” checkbox only and look for “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” in the list of reasons.
- Select this error to view all affected URLs.
- Run the URL Inspection tool to check the indexing and canonical status of individual pages.
How to fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error?
To fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error follow the below steps:
- Set a Canonical Tag on the Original Page: To help Google understand which version of a page should be indexed, you need to add a canonical tag to the correct page version. This tag appears within the head section of your HTML and tells search engines which is the main page.
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.domain.com/preferred-page” />
- Remove duplicate URLs from the XML sitemap: After the canonical tag is set, the next step is to clean up your XML sitemap. Your sitemap should redirect the browser to the canonical versions of each page. This further prevents search engines from indexing unintended versions.
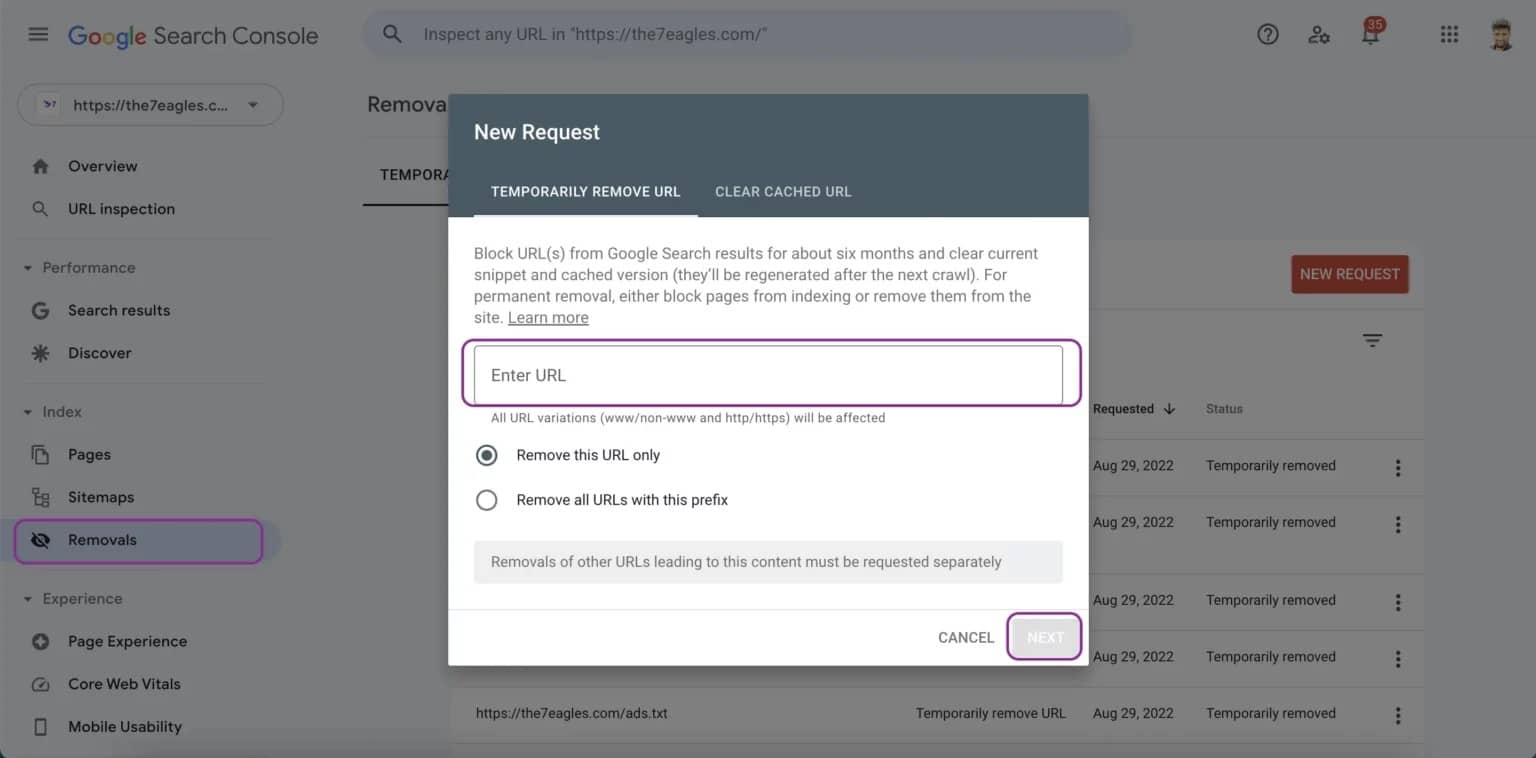
- Redirect Duplicate Pages to the Original: If you have some duplicate pages, redirect them to the canonical page through 301 redirects. This ensures all SEO value is passed to the correct URL and prevents users and search engines from accessing unnecessary duplicate pages.
- Use Google Search Console’s URL Parameters Tool: If your website is generating dynamic URLs through tracking or filter parameters, utilize the URL Parameters tool in Google Search Console. This helps Google understand which parameters are necessary and which ones to ignore which helps in avoiding unnecessary duplication.
- Merge Similar Content Pages: Pages that are nearly identical with minimal content changes, such as the ones targeting different places, devices, or slight keyword variations, should be consolidated into one strong page. It avoids splitting your signals across multiple duplicated pages, reduces redundancy and improves content quality.
- Use Noindex Robots Tag for duplicate pages: If you have duplicate pages that still need to be accessible but shouldn’t appear in search results, simply apply a noindex robots meta tag to all those pages. This will prevent engines from indexing these unwanted pages.
- Validate Fixes in the Google Search Console: Once you have made all the above-mentioned changes, it is important to confirm that Google recognizes them. Use the “Validate Fix” button in the Google Search Console to prompt Google to re-crawl the affected pages and update the status.
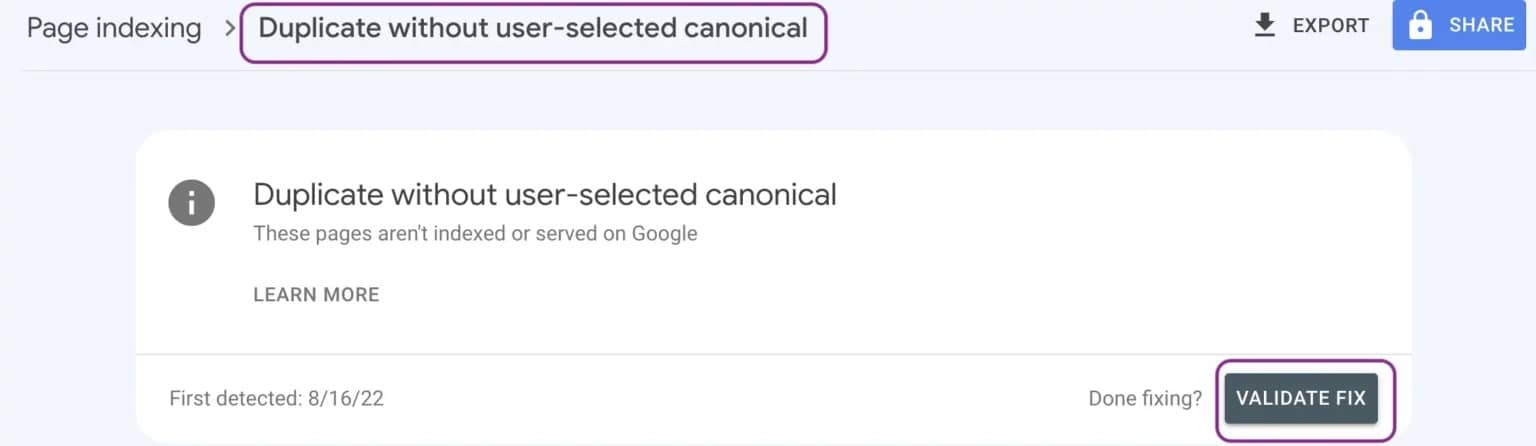
How Long Does it Take for Google to Reindex Fixed Pages?
Google usually takes 1 to 2 weeks to reindex updated pages after you’ve validated the changes in Google Search Console. To speed up the Google indexing process, you can submit an updated XML sitemap. This signals Google that changes have been made and encourages faster crawling.
Conclusion
Fixing the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” issue in the Google Search Console is essential for SEO success. Remember, Google aims to provide the best user experience and credit unique content. Hence, cleaning up duplicate content issues achieves the required goal and opens the path to better visibility.
AlgoSaga a reliable digital marketing agency specialized in resolving technical SEO issues like these. If you need help with fixing SEO issues, contact them for best SEO services today,
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Does the duplicate without canonical error affect SEO rankings?
Yes! If some of the important pages are excluded from indexing, it will automatically hamper your search visibility and reduce organic traffic.
Q2. Should I use canonical tags or 301 redirects for duplicate pages?
If you have duplicate pages that are no longer needed, you can use 301 redirects. Use canonical tags when pages serve different purposes but have similar content.
Q3. How do I know which version of my page is canonical?
You can use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to check which page Google considers canonical.
