Last Updated on July 21, 2024 by Admin
Are you annoyed by frequent technical errors on your website? This refers to one of Google’s most common excluded errors, “duplicate without user-selected canonical,” in the URL inspection results under the indexing—> pages section.
Page indexing is possible; the options are Indexed or Not Indexed. This error is among the reasons it is not indexed due to possible duplicate content or incorrect canonical URLs.
Once you detect this problem on any web pages, you should ask yourself whether the web pages are suitable for indexing. If your answer is NO then it is not an error. However, the following guidelines might help if the answer is YES.
Causes for the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status
The “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error occurs when Google finds multiple pages on your website that have the same or almost the same content but you didn’t select which of the pages would be the main or “canonical” page. Meanwhile, without you indicating which page Google should index, there is a high chance that none of the pages will be indexed.
This mistake may harm your SEO by creating duplicate content and restricting important pages that won’t be indexed and ranked. Therefore, it’s vital to take care of it immediately.
Causes for the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status
Several factors can trigger the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” status:
Content duplication: You can find nearly duplicate content on many site pages, such as posts copied into category archives or the same product description on various URLs.
Canonical tag usage: Failure to canonicalize the tag to indicate your preferred version of the page if it is duplicated or very similar to another page.
Targeting various countries with similar content: This means you use the same pages for each location, which contain location names interchanged with just the location name, and the content remains mostly the same.
Syndicated content. It means replacing it or syndicating the same across different other websites or platforms without showing where the versions came from.
Additional causes can include:
- Conflicting HTTP/HTTPS versions of a page,
- URL parameters,
- WWW vs non-WWW URLs,
- paginated content,
Identifying the specific reason for your site is key to choosing the right fix.
“Duplicate without user-selected canonical” in Google Search Console
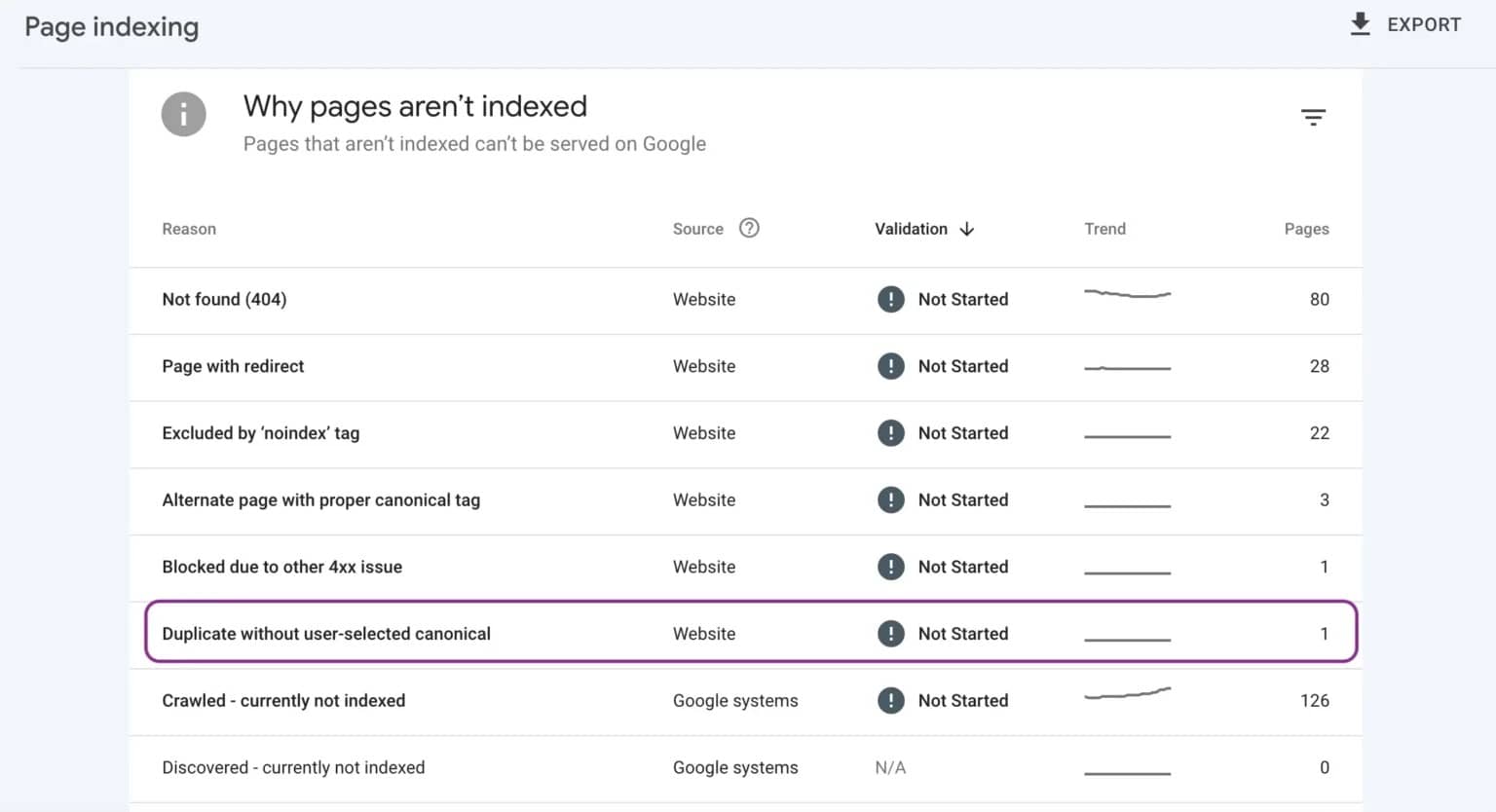
To check if your site has been affected by Duplicate without user-selected canonical:
- Log into Google Search Console, click “Pages,” and navigate to the “Index” section.
- There, you will see a chart of indexed vs not-indexed pages.
- Search the “Not indexed” tab and pick out the phrase “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” among the list of reasons.
- If you see it, click to see sample affected pages.
- In addition, you can run the URL Inspection tool for individual pages and get more information about their indexing and canonicalization status.
How to fix “Duplicate without user-selected canonical”
The important part is dealing with the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” problem. Here are the key steps:
Step 1. Update Canonical Tag for the Original Page: Specify which versions you want indexed by adding a canonical tag to the original page. This tag appears within the head section of your HTML. On the first page, put in the self-referencing canonical URL. For every other page version, use the canonical tag to direct to the source page you designated as the original.
Step 2. Remove the duplicate page from XML sitemap: After the canonical is set, the next step is deleting any duplicate or alternate URLs across your XML sitemap. Instead of linking to the http and https versions, redirect the browser to the canonical URL. This further justifies that one version must be indexed.
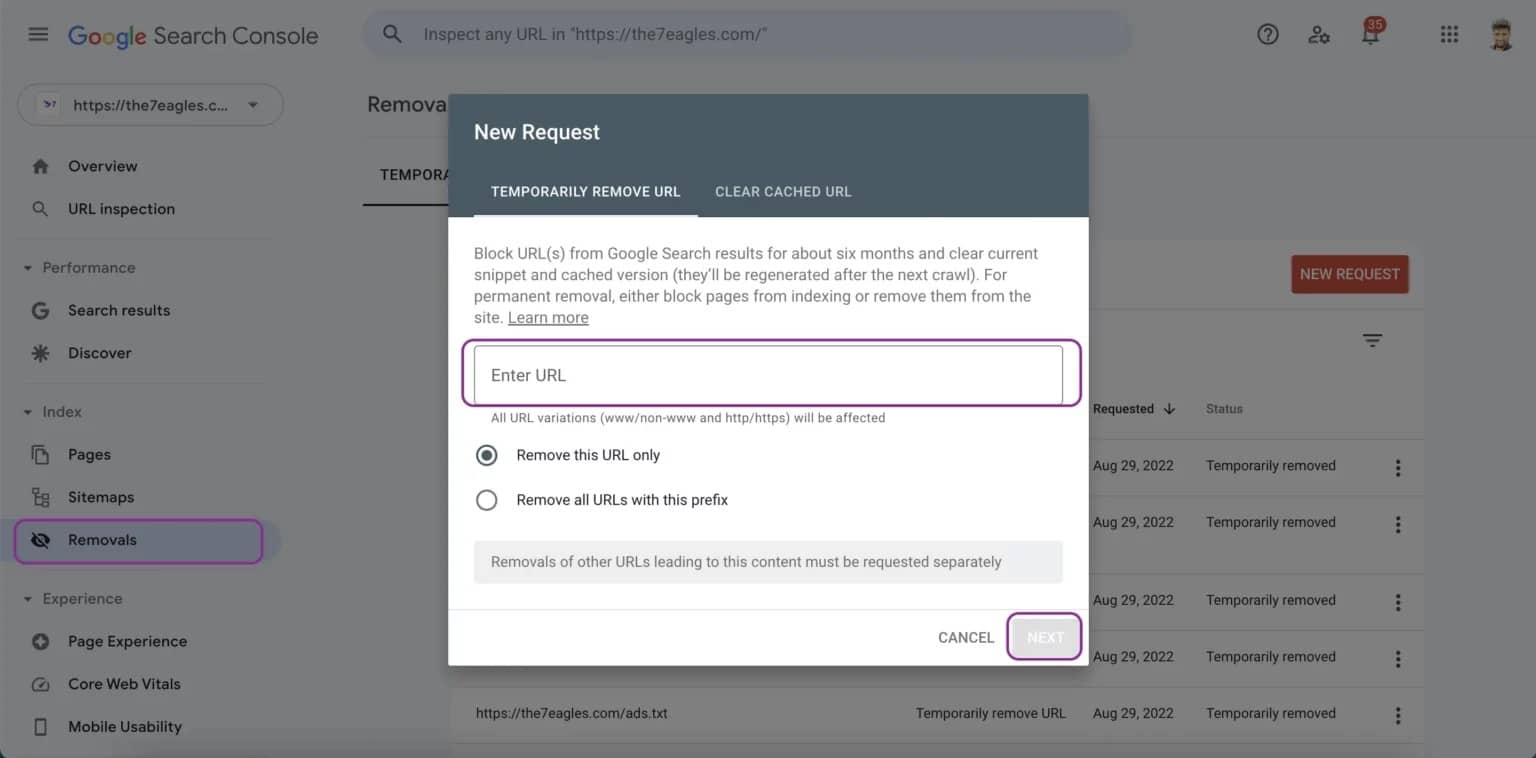
- Go through your sitemap and remove any URL duplicates or alternates of other pages.
- Only keep the canonical version of each page in the sitemap.
- Resubmit the updated sitemap to Google Search Console.
Step 3. Redirect to Original Page: If you have some duplicate pages you no longer require, redirect them to the canonical page through 301 redirects. This is how you manage all signals to your desired URL and thus prevent the duplicates from being accessed.
Step 4. Mention Google search console to ignore URLs with parameters: Use the URL Parameters tool in Google Search Console to block the parameters of your site that are irrelevant to the search engine. It thus combines the URLs with similar parameters, no matter how slight.
Step 5. Consolidate Identical or Nearly-identical contents: Look into merging or consolidating the pages with different places, devices, or slight keyword variations with similar content that does not look original. In general, having one strong page with unique content is more advisable rather than splitting your signals across multiple duplicated pages.
Step 6. Use Noindex Robots Tag for all the duplicate web pages: For the remaining duplicates you find, put a noindex robots meta tag in the head area to ensure that engines do not index that version. Unless it is a non-canonical entry. To do this:
- Identify duplicate pages that will remain accessible but don’t want to be indexed.
- Add a
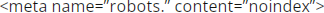 tag to the <head> section of each of those pages.
tag to the <head> section of each of those pages. - Only use noindex on the non-canonical duplicates, not the main version you want indexed.
Step 7. Validate Fix: Then, you should use the “Validate Fix” button in the Google Search Console coverage report to verify fixes. That will cause Google to fetch and crawl your affected pages and update the report to show any resolutions.
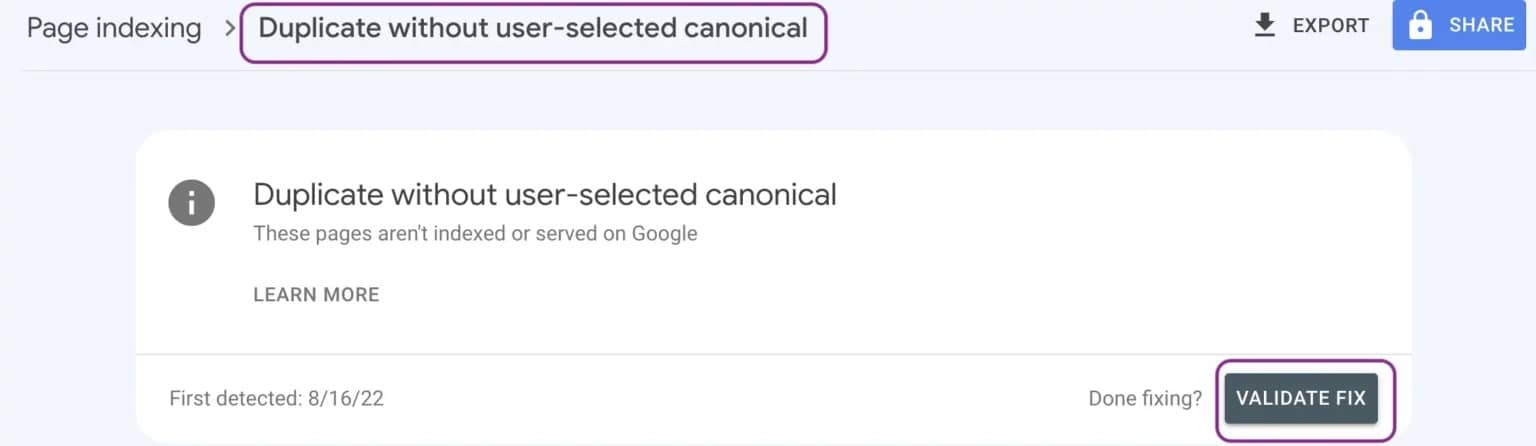
- Go to the Coverage report and find the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” issue.
- Click the “Validate Fix” button to prompt Google to recrawl the affected pages.
- Monitor the report over the next days and weeks to confirm the issue is resolved.
Conclusion
Settlement of the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” problems in the Google Search Console is essential for SEO success. Recall that Google aims to provide the best user experience and credit unique content. The goal is achieved by resolving the duplicate content issues, and the path to better visibility is opened.
At AlgoSaga digital marketing agency, we are professionals in solving SEO technical issues like this and boosting your website’s organic performance. Our team of SEO experts can help you spot and fix indexing issues, optimize site architecture, and implement advanced SEO strategies.
