Last Updated on June 10, 2025 by Admin
What exactly do these 404 errors mean in your Google Search Console, and how can they affect your website? Let’s check out the complete guide to know about them and the proper solutions to address these errors.
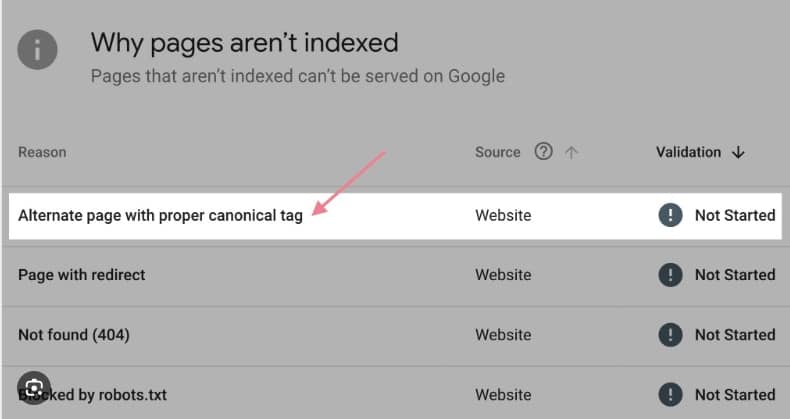
What is 404 Error in Google Search Console?
A Google search console 404 error occurs when Googlebot tries crawling a URL on your site but receives an HTTP response status code of 404. The 404 status code signals that the requested page does not exist on the server. Common triggers are link of deleted pages still listed in sitemaps and internal links to removed pages.
There are many Google search console 404 errors, but some common ones are:
- Deleted Page Still in Sitemaps: A major source of 404s is having deleted pages listed in sitemaps. This tells search engines like Googlebot URLs exist that don’t anymore.

Cross-checking sitemaps against current active pages and deleting old references prevent tons of pointless crawling down.
- Broken Navigation Menu Links: Navigation menus linking to retired pages are another headache. Again, remodeling sites introduce link rot if menus aren’t fully updated.
- Old URLs Shared Publicly: URLs to pages get shared constantly via social media, emails, etc. by visitors. If that new piece of content got removed without redirects, anyone clicking those stale URLs fed into an unpleasant “404.”
- Internal Links to Missing Pages: Review your site content for any outdated links pointing to non-existent pages. Deleting pages without proper redirects or link updates can harm your site’s SEO.
- Fake URLs from Spam Sites: Spam sites or low-quality directories can create fake URLs for your domain and link to those bogus pages. This tricks Googlebot into crawling non-existent paths, leading to 404 errors.
Just ignore these. They don’t indicate website issues on your end. Focus fixes on links you control.
Impact of Google Search Console 404 error
Getting a lot of Google Search Console 404 error can cause issues for your website performance. Few random 404s are no big issue, but a large number of crawling 404 errors in Google Search Console reports might start happening your website’s search engine results. Let’s break down potential problems step-by-step:
- Site Crawl Efficiency: Googlebot has limited time to spend crawling each website it indexes. If it quickly encounters many broken links and “404” messages, Google will assume your site is poorly maintained. As a result, Googlebot may decide to slow down crawling for your website. This can slow down how fast good pages get discovered and indexed from your site.
- User Experience: If internal links on your website consistently lead users to 404 error pages, they’ll become frustrated by the missing content. Excessive 404s degrade the user experience and increase bounce rates. People expect to find what they click on, and giving them dead ends damages your site’s credibility.
- Potential Ranking Drops: Although not a major ranking factor, search engine can view excessive 404 errors as a sign of a low quality website. The crawl efficiency and user experience impact enough your website traffic.
How to Fix 404 Errors in Search Console?
Dealing with many Google search console 404 errors seems complicated, but fixing them is straightforward. Follow this a plan to make 404s broken links disappear:
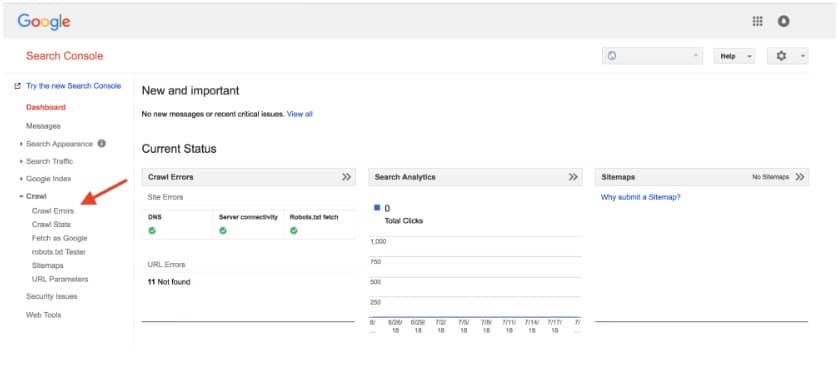
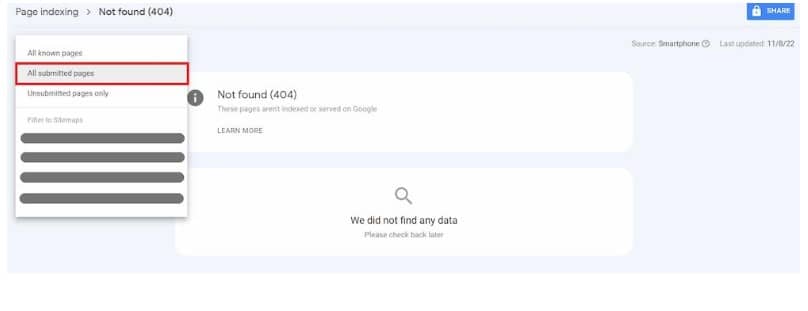
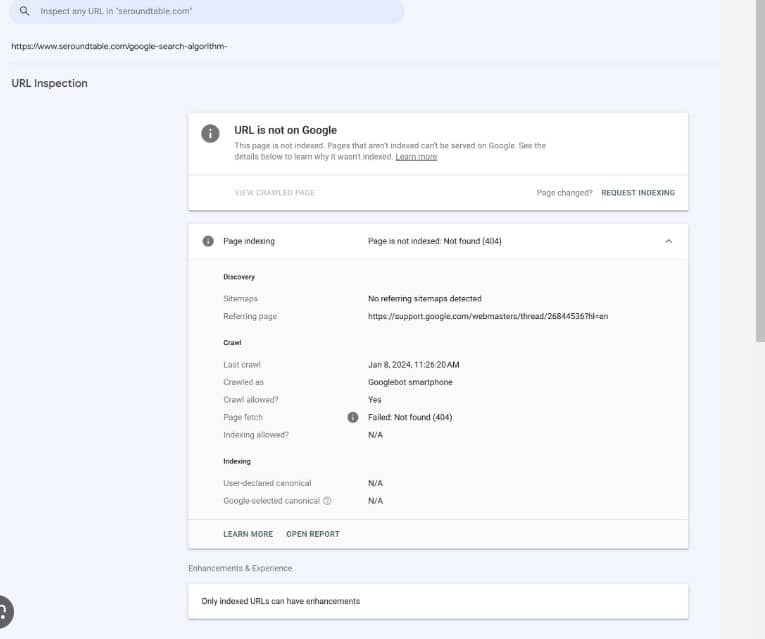
- Find Affected Pages: Open your Search Console and click “Page indexing” > “Not found.” This shows all URLs getting “404 errors”. Export the list, so you have all faulty addresses documented in one place for easier diagnosis and management.
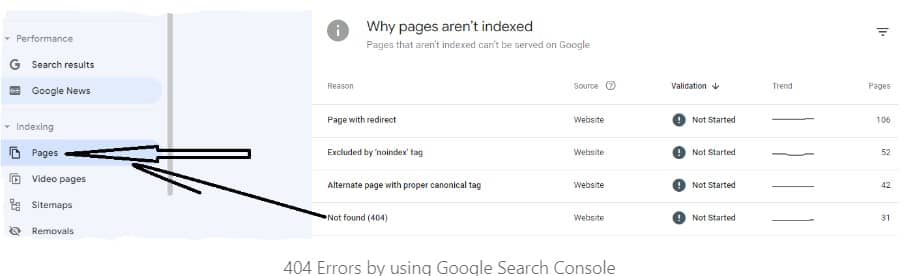
- Delete Broken Links: Next, do a full scan of your website for any links pointing at 404 URLs on your exported list. Double-check XML sitemaps too, since they can contain broken leftovers that send Googlebot to missing pages.
- Create 301 Redirects: If deleted pages were properly moved, then setup 301 redirects from old locations to new ones so search engines and visitors get seamlessly sent to current addresses. Permanent redirects indicate the correct page path has changed while preserving link equity & rankings.
- Fix Simple Errors: Another batch of 404s may result from link typos and URL structure changes after a site redesign. Double-checking these can reveal minor corrections needed.
- Ask Google to Re-Crawl Pages: After fixing the underlying problems, the final step is to request Googlebot to re-crawl all affected areas. Over time, pages returning 200 success status will replace the Google search console 404 error.
Conclusion
Few scattered 404 errors in Google Search Console are normal, but reducing these number through regular link maintenance, accurate sitemaps, and effective redirects strengthens your site’s infrastructure for both users and search engines. If you need professional assistance to resolving persistent 404s reported in your Google Search Console, then contact technical SEO expert at AlgoSaga digital marketing company to help fixing them.
